“Simplify WordPress” is our series of creating shortcut methods.
Ch.1 – Customizer API
Ch.2 – Custom REST API
Ch.3 – Post Table (coming soon)
Have you ever tried modifying the Customizer section? If yes, you definitely noticed how unnecessarily complex it is.
In this tutorial we will take a look at how to simplify it.
Terminology
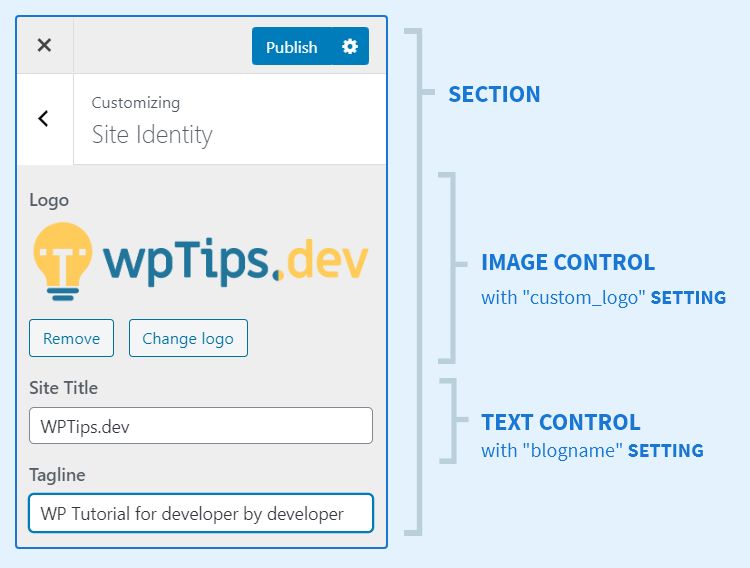
- SECTION – Group of settings.
- CONTROL – The input method of your setting.
- SETTING – What’s saved in the database. There are two types of setting:
- THEME MOD – Bound to the theme. Changing theme will reset this.
- OPTION – Bound to the site. Changing theme will not affect this.
The Original Method
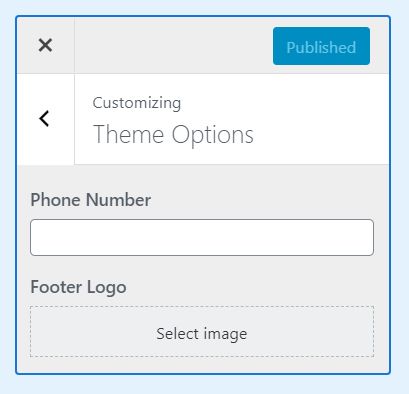
Let’s say we want to create a Theme Options section that contains phone number and footer’s logo. Here’s what it looks like and the code:
add_action( 'customize_register', 'create_theme_options' );
function create_theme_options( $customize ) {
// Create section
$customize->add_section( 'theme_options', [
'title' => __( 'Theme Options' ),
] );
// Create setting for Phone Number
$customize->add_setting( 'phone_no', [
'type' => 'theme_mod',
] );
// Create text control, assign 'phone_no' setting
// and place it in 'theme_options' section
$customize->add_control( 'phone_no_control', [
'label' => __( 'Phone Number' ),
'type' => 'text',
'section' => 'theme_options',
'settings' => 'phone_no',
] );
// Footer logo
$customize->add_setting( 'footer_logo', [
'type' => 'theme_mod',
] );
$customize->add_control(
new WP_Customize_Image_Control(
$customize,
'footer_logo_control',
[
'label' => __( 'Footer Logo' ),
'section' => 'theme_options',
'settings' => 'footer_logo',
]
)
);
} // close functionIn my opinion, those methods are too wordy and repetitive. Having to define the Setting and Control method separately is also questionable.
Our Simplified Methods
We have created a helper class that mimics the functionality of the original:
require_once __DIR__ . '/my-customizer.php';
add_action( 'customize_register', 'create_theme_options' );
function create_theme_options( $customize ) {
$customize = new MyCustomizer( $customize );
// No need to define title, it will be derived from the slug
$customize->add_section( 'theme_options' );
// Setting and Control method are combined
$customize->add_setting( 'phone_no', [
'type' => 'theme_mod',
'control' => [
'type' => 'text',
'section' => 'theme_options'
]
] );
// No longer need to pass in a Class object to define Image control
$customize->add_setting( 'footer_logo', [
'type' => 'theme_mod',
'control' => [
'type' => 'image',
'section' => 'theme_options'
]
] );
}Available input types:
textselect– requirechoicesargument that containsvalues => labelsarray.radio– also requirechoicesargument.checkbox– just a single on/off checkbox.textareadropdown-pagesemailurlnumberhiddendateimagecropped_image– Image that allows cropping. Detail here »coloruploadvisual_editor– textarea with bold, italic, etc.code_editor– requirecode_languageargument with possible value: clike, css, diff, htmlmixed, http, javascript, jsx, markdown, gfm, nginx, php, sass, shell, sql, xml, and yaml
Conclusion
Customizer is an underused feature in WordPress. There are many reasons, but being harder to modify than a traditional Setting page is one of them.
Hopefully with this helper class, you can give Customizer a try and see how useful it is.
In Chapter 2, we will take a look at the dreaded Post Admin Table API.
Let me know in the comment below if you have feedback or question regarding Customizer API 🙂
Useful Links:




